
Road Safety Manual
A manual for practitioners and decision makers
on implementing safe system infrastructure!

Road Safety Manual
A manual for practitioners and decision makers
on implementing safe system infrastructure!
Once the problem type has been identified (whether through crash analysis or other forms of risk assessment), the next step in the process involves the selection of an appropriate intervention. The main aims during this stage are:
There are a number of issues to consider when selecting interventions. Usually cost and economic efficiency are the first and foremost considerations, but there are also others. It is important to ensure that the intervention is cost-effective and gives a positive benefit-cost ratio, and that it can be implemented within the available budget. Based on issues identified by Ogden (1996) and BITRE (2012), other considerations include:
A ‘hierarchy of control’ is often used in risk assessment when selecting and prioritising interventions. As an example, Marsh et al. (2013) suggest that such a hierarchy helps identify a priority order for different types of road safety treatment based on outcomes. They suggested a road engineering hierarchy based on the Safe System approach to help address driver distraction and fatigue. The hierarchy has four levels, and it is suggested that level 1 equates to a level of risk where Safe System outcomes are likely:
There are a large number of safety interventions that can be used to improve road safety. Some have only a small impact on safety, while others can produce substantial reductions in death and serious injury. The concept of ‘high-performing’ infrastructure was introduced in The Role of Safer Infrastructure in Safe System Elements and application, and has been discussed in the context of the Safe System approach in several documents. For example,
Turner et al. (2009) present a framework for Safe System infrastructure solutions based on major crash types with a distinction between ‘primary’ and ‘supportive’ road safety treatments.
Primary treatments are those that have the potential to achieve Safe System outcomes or near-zero deaths and serious injuries. This can be achieved through reducing impact forces to safe levels or by separating different road users. A supportive road safety treatment is one that assists with the delivery of safety improvements, but only in an incremental way. For example, a hazard warning sign may reduce the occurrence of crashes (which can include severe crashes), but will have no impact on the severity of a crash, should one occur.
It is strongly recommended that primary treatments are employed where possible to reach the Safe System objectives. ‘Primary’ or ‘Transformational’ treatments should be presented as a first option. If these cannot be used, there would be a preference to next consider treatments that might be a stepping stone with minimal redundancy of investment, to future Safe System implementation. For example, a wide central painted median with audio-tactile lines may be installed with adequate width to allow future application of wire rope median barrier. Primary or ‘Transformational’ treatments to address key crash types are demonstrated in Table 11.1
Crash Type | Treatment “Primary” or“Transformational” | Influence (E = exposure L = likelihood S = severity) |
Head-on |
| L S S L, S |
Run-off-road |
| S S
L, S |
Intersection |
| L, S E L, S L, S L, S |
Pedestrian / Cyclist |
| E L S L, S |
Motorcyclist |
| E
|
(Source: Adapted from Austroads, 2016)
Below are some further examples of illustrated primary Safety System treatments (Figure 11.3)



Issues specific to LMICs regarding the use of such treatments are discussed further in Intervention Effectiveness in LMICs in Intervention Option and Selection.
NZTA (2011) refers to Safe System Transformation treatments for rural roads. These are defined as treatments that are likely to address high percentages of the fatal and serious injury crashes associated with of the three key crash types for rural roads (run-off-road, head-on and intersection crashes). It is recognised that these treatments are typically higher cost, and that they need to be implemented over a longer time period. Examples of such treatments include expressways (4-laning and 2+1 treatments), median and roadside barriers, grade separation (overpasses and interchanges), roundabouts, and effective speed management. New Zealand also provides a framework that encourages investment in Primary or “Transformational” treatments as standard safety interventions (NZTA, 2021).
The following case studies in Hungary demonstrate innovative use of primary Safe System treatments in a temporary, or low cost, application.
Where a primary solution is not feasible due to project constraints dictated by budget, site, conflicting road user needs, or the environment, the next safest “supporting” Safe System solution needs to be identified. Ideally, supporting treatments should act as stepping stones towards better Safe System alignment and be compatible with future implementation of Safe System options. In most cases, supporting treatments are those that reduce the likelihood of a crash but do little do reduce the severity outcome. For example, a wide centreline will help to reduce the probability of a crash by providing greater separation between opposing traffic flows. However, when a crash occurs the severity of injury is still likely to be high.
The case study from the Germany provides an example of a supporting Safe System treatmnt through the use a painted wide centreline to support overtaking and separate opposing traffic flows.
Supporting treatments that are compatible with future implementation of Safe System options are demonstrated in Table 11.2.
Crash Type | Treatment “Supporting” (compatible with future implementation of Safe System options) | Influence (E = exposure L = likelihood S = severity) |
Head-on |
| L L |
Run-off-road |
| S
L L, S |
Intersection |
| L, S
E L, S
|
Pedestrian / Cyclist |
| L, S L E L E, L
|
Motorcyclist |
| L
|
There are numerous additional supporting treatments that have little or essentially no effect on future implementation of primary Safe System options such as consistent delineation, skid resistance improvement, improved superelevation, audio-tactile edge and centre lines, vehicle activated signs, turning lanes, advanced direction signage and warning, improved site distance, traffic signals with fully controlled right turns, skid resistance improvement, improved street lighting, pedestrian and cyclist signals, cyclist box at intersections, and motorcycle-friendly barrier systems (Austroads, 2016).
Where high risks are present for more than one crash type (as is often the case), combinations of one or more of treatment should be considered. In addition, combinations of supporting treatments, particularly in association with lower speeds, may be adequate to fully address specific crash risks.
Other measures that should also be considered to further mitigate crash risks, particularly in combination with supporting treatments, include speed enforcement, rest area provision, speed cameras combined with red light cameras, lane markings compatible with in-vehicle lane-keeping technology (Austroads, 2016).
One of the most important considerations in selecting interventions is knowledge of the safety benefit of that treatment. This benefit is often described as a crash reduction factor (the expected percentage reduction in crashes), or crash modification factor (CMF, which is the multiplier by which the crashes before treatment are adjusted; e.g. a CMF of 0.8 indicates that there will be an expected reduction of 20% in crashes). A number of sources exist that provide information on this issue (also see Box 11.1):
The Crash Modification Factor (CMF) Clearinghouse (http://www.cmfclearinghouse.org/) is one of the most comprehensive and advanced sources of information on road safety infrastructure effectiveness. Funded by the US Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), it provides a searchable database of information on infrastructure effectiveness. It is constantly updated, meaning that it is one of the most up-to-date sources of information on this topic. The CMF Clearinghouse applies a star rating (from one to five) according to the robustness of each CMF. This rating was updated to be based on study design, sample size, standard error, potential biases, and data source.
Given the objective of the Safe System approach is to eliminate death and serious injury, it is important to understand the effect that different interventions have on fatal and serious outcomes. However, much of the research on intervention effectiveness provides information on casualty reduction (i.e. reduction in deaths, serious injury and minor injury combined) or on change in all crashes (including non-injury). This is an important distinction, and it is unfortunate that information on fatal and serious outcomes is so scarce. Although it is desirable to minimise all crash types, including crashes that do not result in injury, an overall reduction in fatal and serious injury is paramount. Safety professionals should not be put off using interventions that have a neutral effect on minor and non-injury crashes, and there may actually be situations where such crashes will increase (typically through a reduction in severity of the crashes that do continue to occur at a treated location).
In the absence of information on the effect of interventions on fatal and serious crash outcomes, information on casualty reduction should be used, although an element of engineering judgement may also be required when using this information. The expected reduction in fatal and serious crash outcomes is often higher than the reduction in all casualties. As an example, BITRE (2012) found the impact on crashes from installation of roundabouts to be greater for higher severity outcomes:
Similar trends were seen in a European study by Jensen (2013). Therefore, using the casualty reduction will often lead to a conservative value for the expected reduction in fatal and serious injury.
The following matrix (Table 11.3) provides a basic summary of road safety treatment options and their effectiveness on some of the key crash types that result in fatal and serious injury. Detailed information on each of these treatments can be found in the documents referenced in Selecting Interventions in Intervention Option and Selection. Broad indicative costs are also provided.
Table 11.3: Road safety countermeasures matrix
1. head on
2. Junction
3. rear-end
4. run-off-road
5.Motorcycle
6.pedestrians
| Treatment | Crash type | Cost | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | ||
60% or more expected casualty reduction | |||||||
Intersection – roundabout | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Median barrier | ✓ | ✓ | $$ | ||||
Pedestrian crossing – grade separation | ✓ | $$$ | |||||
Pedestrian footpath | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Railway crossing control | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Roadside safety – barriers | ✓ | $$ | |||||
25–40% expected casualty reduction | |||||||
Additional lane | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | ||||
Motorcycle lanes | ✓ | $$$ | |||||
Duplication | ✓ | $$$ | |||||
Intersection – grade separation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | |||
Intersection – signalised | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Lane widening | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $$ | |||
One-way network | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | |||
Pedestrian crossing – unsignalised | ✓ | $ | |||||
Pedestrian crossing – signalised | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Pedestrian refuge island | ✓ | $ | |||||
Realignment – horizontal | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | ||||
Restrict/combine direct access points | ✓ | ✓ | $$ | ||||
Roadside safety – hazard removal | ✓ | $$ | |||||
Service road | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | ||||
Shoulder sealing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $$ | ||
Skid resistance | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |
Speed management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ |
Traffic calming | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $$ | |
10–25% expected casualty reduction | |||||||
Central hatching | ✓ | ✓ | $ | ||||
Central turning lane (full length) | ✓ | ✓ | $ | ||||
Delineation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | ||
Intersection – delineation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |||
Intersection – turn lanes (unsignalised) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |||
Intersection – turn lanes (signalised) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |||
Parking improvements | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |||
Realignment – vertical | ✓ | ✓ | $$$ | ||||
Regulate roadside commercial activity | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | $ | |||
Rumble strips | ✓ | ✓ | $ | ||||
Side-slope improvement | ✓ | $$$ | |||||
Note: $ = low cost; $$ = medium cost; $$$=high cost.
As can be seen from Table 11.3 speed management is a treatment that is able to address most key crash types. Where speed has been identified as an issue, speeds can be lowered using effective speed management. This will result in fewer fatalities and serious injuries, provided compliance is high or additional enforcement measures are utilised.
The following case studies from Puerto Rico, Portugal, Slovakia, Italy and Hungary all show examples of the effective use of interventions to improve safety.
As can be seen from Table 11.1 speed management is a treatment that is able to address most key crash types. Where speed has been identified as an issue, speeds can be lowered using effective speed management. This will result in fewer fatalities and serious injuries, provided compliance is high or additional enforcement measures are utilised.
Selecting Interventions
Interventions should be selected to suit a particular site, route or area, and to address the crash type occurring at that site, route or area. Crash types can be identified through reactive (crash based) or proactive identification methods (see Assessing Potential Risks And Identifying Issues).
Single interventions can be used, or more commonly combinations of interventions can be selected to combat a particular crash type or issue. The final intervention selection requires expert judgement about the factors that have contributed or may contribute to the occurrence of crashes.
A number of guides provide advice on appropriate interventions to address specific crash problems. PIARC (2023) provides details of road safety countermeasures based on the Safe System approach that have proven track records of success in multiple countries. The effectiveness of each proven countermeasure is noted including recommendations on crash reduction and strategies for practitioners to consider as part of implementation. The countermeasures have also been categorised based on how they address key Safe System principles, such as reducing severity, as well as targeting key crash types and vulnerable road users.
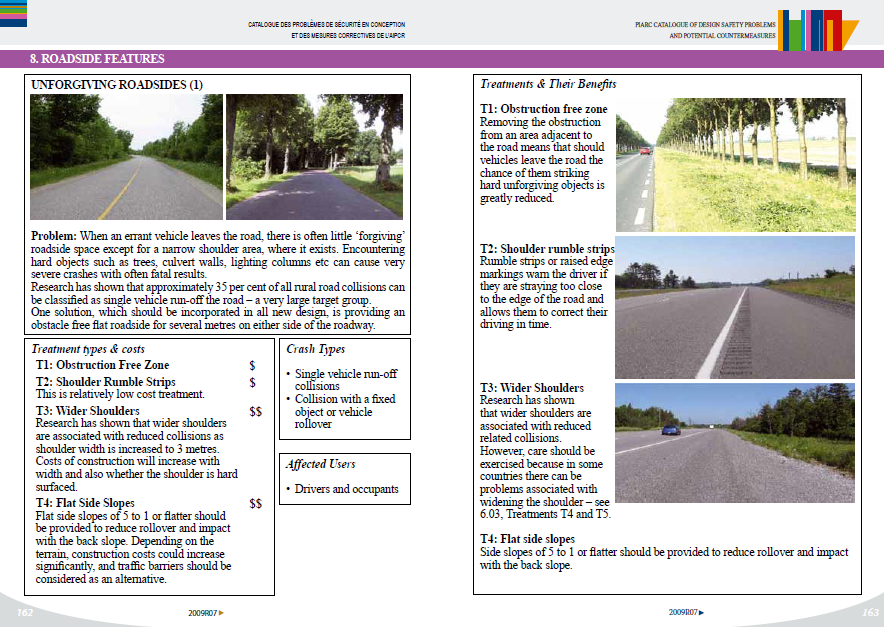
PIARC (2009) provides a detailed set of options in the Catalogue of design safety problems and potential countermeasures. Advice is provided for road function, cross-section, alignment, intersections, public and private services, vulnerable road users, traffic Signing and marking and roadside features. PIARC published The role of Road Engineering in Combatting Driver Distraction and Fatigue Road Safety Risks to highlight Driver Distraction and Fatigue from the view of the safe systems approach. Figure 11.4 shows an example of Hierarchy Level 1 Treatments. The document outlines a hierarchy of treatment approaches and provide engineering solutions to address the problem of driving distraction and fatigue road safety risks. To highlight the issue potential countermeasures for vulnerable road users the Vulnerable road users: Diagnosis of design and operational safety problems and potential countermeasures and appendix were published.
A number of interventions are presented that address safety issues relating to each of these topics. In each case, information is provided on the road safety problem for each issue. Treatment types are then presented, along with photos of the treatment, basic descriptions, indicative costs, crash types addressed, and the affected road user groups. The example below (Figure 11.4) shows potential solutions for issues related to unforgiving roadsides (categorised under Roadside Features).
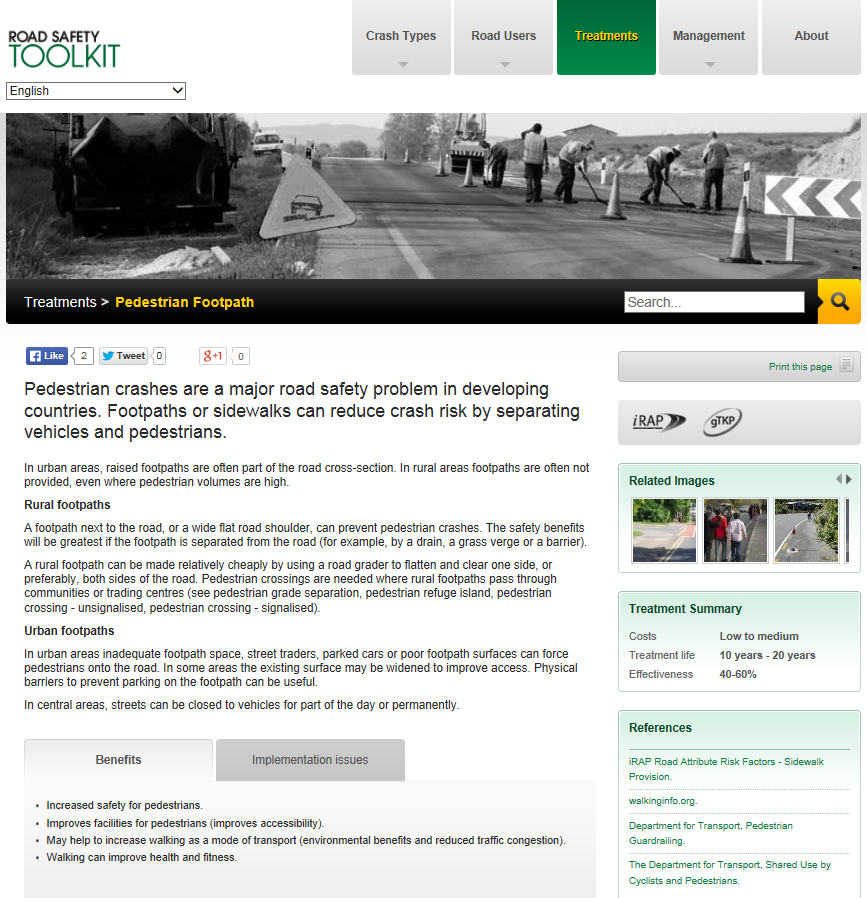
Several online tools exist that provide similar, and in some cases more detailed information. Some cover a wide variety of treatment types, while others concentrate on particular crash types. Both Austroads (engtoolkit.com.au) and iRAP (toolkit.irap.org) have developed online toolkits that provide guidance on treatment options to address different road safety issues. They are both regularly updated and revised, capturing the most recent findings in road safety. Each includes detailed information on crash problem types and treatments, including indicative costs, safety and other benefits, implementation issues, and references.
The Austroads toolkit is designed to address safety issues identified through crash investigation and road safety audit (safety deficiencies). Detailed information is provided on solutions, including links to relevant design documents. The Road Safety Toolkit is targeted to those working in LMICs, and has been translated into a number of languages, including French, Arabic, Spanish and Mandarin. An image from this toolkit is shown in Figure 11.5.
The approach described here builds upon work completed by William Haddon who developed the Haddon Matrix (see Haddon, 1972, 1980). The Haddon matrix provides a tool for looking at factors related to personal attributes, vehicle attributes and environmental attributes before, during, and after a crash. The goal was to have the safety professional consider driver confusion, misperceptions, workload, distraction, and other factors.
The Haddon Matrix considers three phases of a crash 1) Pre-crash which includes those factors that influence whether a crash will occur and then result in injuries: 2) The crash event phase reviewing those factors that will influence crash severity during the crash event; 3) The post crash phase the influence the survivability of crash after the event. To this Milton and van Schalkwyk (2022) expanded on the matrix to provide a framework the directly considered all road users (e.g., the volume of biking and walking) as well as the supporting social safety environment -- consistent with the Safe System approach -- added user mix considerations and interactions between these factors to Campbell et. al., Human Factors Interaction Matrix (2018). The figure below shows the Modified-Haddon Matrix applied to motor vehicle crashes in the Safe System.
Campbell points out that by introducing social environment factors, safety professionals are asked to consider the implications of attitudes, biases and equity decision-making frameworks for humans operating in the roadway environment. Diagnostic assessments are expanded in the effort to incorporate this information. The assessment approach considers laws to reduce severity or frequency of crashes and the road user's willingness to accept those laws and how each of these can be used to address potential safety outcomes.
Equity is considered by assessing more than just vehicles, because one cannot always assume access to vehicles or personal protective equipment., especially within communities that might be lower income or overburdened, and where they cannot purchase a vehicle, bicycle or other protective devices. In many lower income and minority communities sidewalks and lighting may not exist, which leads to lower level of safety and security.
Road user mix is an important consideration as all road users must interact within the context and road environment. For instance, considering how a pedestrian ability to view closing distance and visibility on a rainy day may be negatively affected and lead to increased crash potential.
Although the focus of this manual is on infrastructure interventions, it is important to ensure that multi-sector approaches (e.g. those involving education and enforcement) are considered, as these will often have a greater impact on safety than infrastructure measures alone. This is especially the case in LMICs where there may be lower levels of compliance, or less understanding by the general public regarding the intent of safety interventions. Issues specific to LMICs and intervention effectiveness are discussed in Intervention Effectiveness in LMICs in Intervention Option and Selection while the following case study provides an example of a combined infrastructure and education programme to address pedestrian safety in South Africa.
As another example, the SURE handbooks (particularly the handbook ‘Plan d’actions et realisation des actions’) provide guidance on the French methods for selecting safety interventions on the network (see Box 9.8).
Most of the information on intervention effectiveness is based on research conducted in HICs. Aside from research on behavioural interventions in LMICs, there are very few studies on the effectiveness in these countries, especially the effectiveness of road safety infrastructure treatments. This issue is significant, as it cannot be expected that interventions used in HICs will have the same outcomes when used in LMICs.
This issue has been highlighted in several studies. OECD/ITF (2012) suggests that there are many context/environment-related elements that influence actual crash reduction, and that this is a more critical consideration in LMICs. For example, provision of a hard shoulder might improve safety in a HIC. However, in a lesser developed country it might encourage improper use, such as the installation of stalls for selling items to travellers, which could decrease the overall safety of the roadway. An understanding of these issues of context is obviously critical to the successful implementation of safety treatments.
There also appear to be several barriers to the successful implementation of road safety infrastructure treatments. Turner & Smith (2013) conducted a workshop to identify issues around the implementation of infrastructure treatments in LMICs. Several effective infrastructure treatments were discussed, and barriers for each explored. Although a number of issues were identified for each treatment type, many of these fell into similar categories. These included cost, issues with compliance, design and implementation issues, public acceptance and maintenance.
Cost was raised as an issue for many of the treatments, although interestingly not for all. For some of the highly effective treatments, cost does not appear to be a significant issue. Of greater interest is that issues relating to compliance and design/implementation were raised for more of the treatments than cost. Compliance of treatments by road users is a significant issue in LMICs, and it is very likely that the treatment effectiveness will be lower as a result. Issues that suffered from this compliance issue were:
This issue of compliance indicates the need for a multi-sector response to the road safety issue. The use of safer infrastructure needs to be supported by appropriate education and enforcement, as discussed earlier in this manual.
Design and implementation issues were also thought to have an impact on the effectiveness of treatments. If a treatment is not well-designed and the installation is not of a high standard, the crash reduction potential will not be met. This was considered an issue for all of the treatments discussed. This situation can only be improved through improving the skills and capacity of those working in LMICs, including the sharing of knowledge regarding good practice.
Lastly, maintenance is also an issue that will impact on the crash reduction effectiveness of treatments. It is common for treatments to deteriorate to levels where they become less safe (or possibly to a point where they are higher risk than if the treatment was not present). Appropriate funding is required to ensure that treatments are maintained. Training may also be required regarding the issue of maintenance.
Although all of these issues are likely to be concerns for HICs, they are possibly more pronounced in LMICs, and will certainly have an impact on treatment effectiveness. The extent of this effect is not known, but it can be expected that because of these issues, treatment effectiveness is likely to be different (typically less) than when the same treatments are used in HICs.
Given the absence of good information on treatment effectiveness in LMICs, it is recommended that crash reduction values from HICs be used as a starting point when selecting treatments. However, the issues discussed above need to be carefully considered, and appropriate revisions made to expected benefits. In the longer term it is hoped that the knowledge base regarding treatment effectiveness in LMICs will improve, but this will only occur if appropriate monitoring, analysis and evaluation occurs in these countries (see Monitoring, Analysis and Evaluation of Road Safety). The case study from Puerto Rico shows the effective use of rumble strips to lower roadway departure crashes.
They will be required in order to help eliminate death and serious injury. Many safety treatments currently result in some residual serious crash outcomes, and so improvements to current treatments will be required. As treatments are applied to new situations (including in LMICs) there will be a need to adapt them for better outcomes. There are also a number of highly effective interventions that exist and are used in some countries but not at all in others. There is a need for road agencies and supporting organisations to be innovative and adopt new approaches, provided these are implemented based on an evidence-led approach. It is recommended that road agencies investigate new interventions and learn from overseas experiences.
Reasons that some highly effective treatments are not used in some countries include:
Road agencies should be careful in their selection of new treatments, ensuring that they have been rigorously tested and have demonstrated safety benefits. Demonstration projects can be an effective way to assess promising treatments, and prepare for a wider roll-out (see Strengthening Capacity to Set and Deliver Targets.)
It is suggested that a methodological approach be taken towards innovation, outlined in the following steps:
A number of the reference documents highlighted earlier in this chapter provide innovative examples of road safety infrastructure treatments. Some agencies actively promote certain treatments (including innovative ones) that they would like to see used more often (e.g. FHWA, 2015, which documents and promotes proven safety countermeasures; while information on innovative intersection design including videos can be found here: http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/everydaycounts/edctwo/2012/geometrics.cfm). Many national and local studies have been undertaken to assess innovative treatments with promise. These studies are usually undertaken by universities and research institutes. Information on these trials can be found in international journals and at conferences, although care should be taken to ensure that such information is robust.
The case studies below provide an example of innovative use of intelligent transport systems (ITS) in Thailand and pedestrian and cyclist crossings at tram and transit lines in Germany.